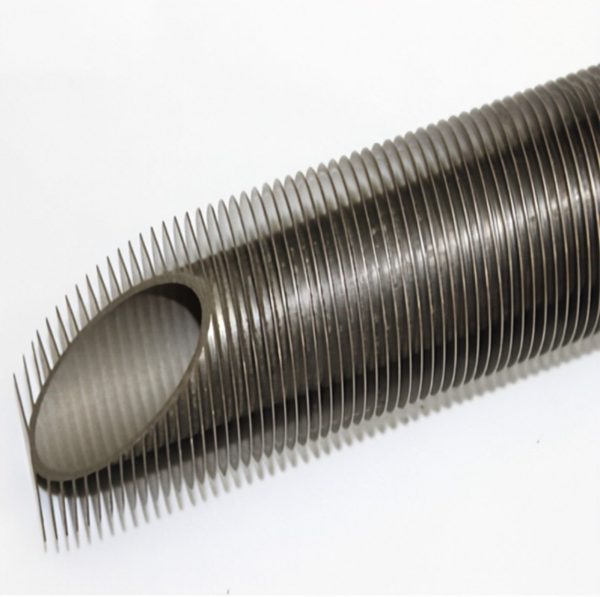
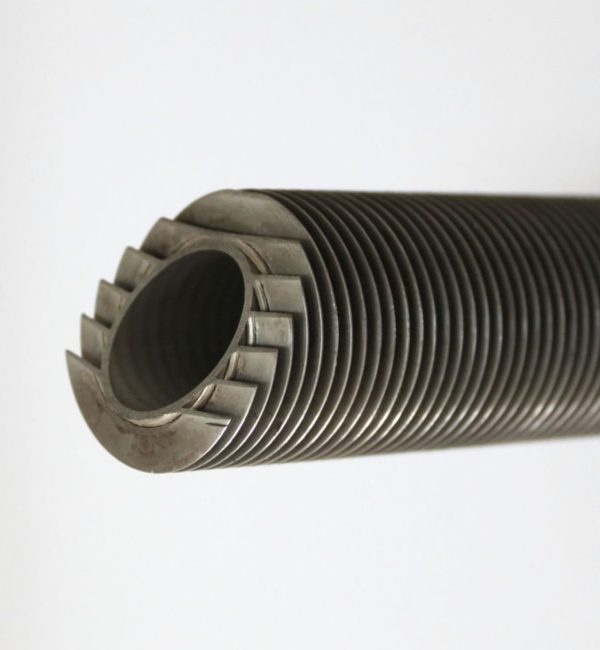
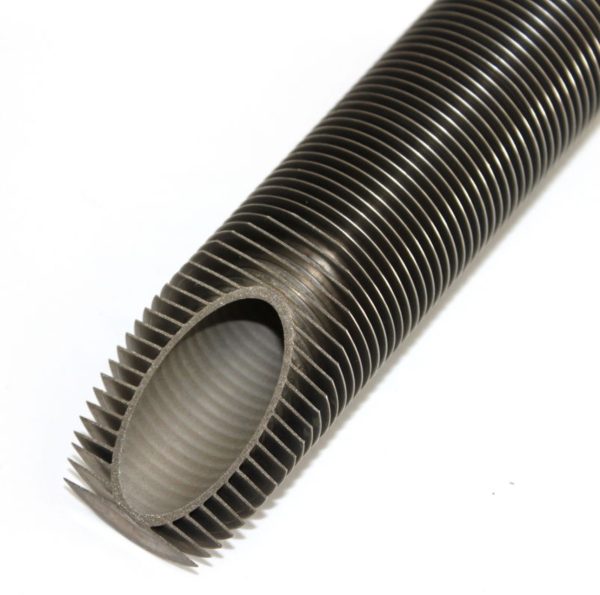
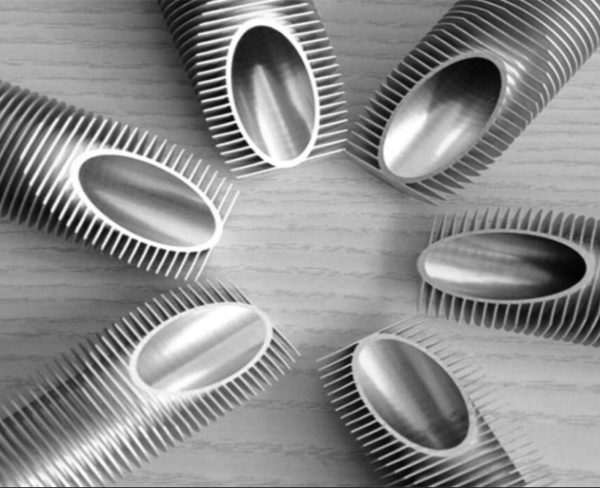
Titanium Fin Tube
Titanium fin tubes are a type of heat exchanger used in many industries. They are made of titanium. The fins increase the surface area of the tubes, which allows them to transfer heat more efficiently and the weight is light compare with other materials. This makes them ideal for applications where high heat transfer rates are required.
Finned tubes are used in applications that involve the transfer of heat from a hot fluid to a colder fluid through a tube wall. They are used in condensers, coolers, and furnaces. The larger surface area means that fewer tubes are needed compared to the use of plain tubes.
The type of finned tube is chosen depending on the specific requirements of each process equipment unit. The fin type and combination of materials are chosen based on the specific requirements of each process equipment unit.
- Description
- Inquiry
Description
Titanium fin tubes are widely used in a variety of heat exchanger applications worldwide. These applications cover many industries such as steam turbine power plant, refineries, chemical plants, air conditioning systems, multi-stage flash distillation, desalination and vapor compression plants, offshore platforms, surface ships and submarines, as well as swimming pool heating systems. The popularity of titanium tubes results from several fundamental reasons:
1. Excellent Corrosion Resistant
Due to the high affinity of titanium to oxygen and moisture in the air, a highly stable, tenacious and permanent thin oxide film (TiO2) forms on the metal surface and immediately regenerates after being damaged. This property explains the excellent corrosion resistance of titanium to a plurality of harsh environments such as oxidizing chloride solutions, acetic and nitric acids, wet bromine, and acetone. Titanium is further very stable in formic, citric, tartaric, stearic, and tannic acids. Alkaline environments up to pH 12 and 75°C usually offer no problem for titanium. Titanium is used in areas in which austenitic stainless steels no longer provide sufficient corrosion resistance.
For heat exchangers in which the cooling medium is seawater, brackish water, or polluted water, commercially pure titanium tubes have demonstrated their superior corrosion resistance for decades. Usually titanium requires no corrosion allowance, so often the higher up-front costs are compensated soon by less down time and reduced maintenance costs.
2. Proper Mechanical and Physical Properties
The thermal conductivity of titanium is roughly 50% higher than for stainless steel. It makes titanium a preferred material for heat exchangers. The high specific strength (strength-to-weight ratio) characterizes titanium for some applications where less mass are required. Engineering experiences have shown that titanium exhibits good erosion resistance. Even water speeds of 10 m/s do not cause any erosion corrosion, cavitation, or impingement attack in the tubes. Thus, thin-walled heat exchanger/ condenser tubing can often be used with zero corrosion allowance.
Why use finned tubes?
Finned tubes are used in applications where high heat transfer rates are required, such as in power plants and refrigeration systems. The fins increase the surface area of the tube, allowing for more efficient heat transfer between two fluids. This makes them an ideal solution for heat transfer applications where space is limited.
Finned tubes are used in condensers, coolers, and furnaces. The larger surface area means that fewer tubes are needed compared to the use of plain tubes. This can decrease the overall equipment size and can in the long-run decrease the cost of the project.
Finned tube heat exchangers can be used in a broad range of industries including oil & gas, power generation, marine and HVAC&R. They generally use air to cool or heat fluids such as air, water, oil or gas, or they can be used to capture or recover waste heat.
The biggest problem with using a finned tube heat exchanger is with the cleaning and maintenance of the outer surface of the tubes. Because of the fins, mechanical cleaning becomes very difficult and you would have to go for chemical cleaning.
What is the difference between fin tube and finned tube?
Fin tubes are a type of heat exchanger that are used in many industries. They have a finned surface, which increases their surface area and allows them to transfer heat more efficiently. Finned tubes are typically used in two-phase heat transfer applications, such as condensation or evaporation.
Finned pipes are generally used for single-phase heat transfer applications. Both finned pipes and finned tubes use fins to increase the surface area for heat transfer.
Finned tubes are used when the heat transfer coefficient on the outside of the tubes is appreciably lower than that on the inside. They can reduce the equipment cost and also equipment sizes.
There are several kinds of fin tubes, such as:
- Extruded fin tube
- Crimped spiral fin tube
- G type embedded fin tube
- L/KL/LL Foot Fin Tube
What is the difference between high fin and low fin tubes?
High fin tubes are better for applications where the temperature difference between two fluids is high. Low fin tubes are better for applications where the temperature difference is low.
High fin tubes are made of a metal tube surrounded by an aluminum or copper strip. The strip can be applied in different ways, including type L, type KL, type LL, type G (embedded), or type extruded. The higher the fin height, the more surface area and heat transfer capabilities.
Low fin tubes are made of a single material and have a smaller fin of about 1/16th of an inch. They are generally used in liquid to liquid or liquid to gas applications such as coolers, condensers, and chillers.
The profile of the fins has a significant effect on the performance of a finned tube heat exchanger. The larger the fins and the tighter the fin pitch, the more thermal conductivity is achieved.
What is the role of finned tube in heat transfer?
Finned tubes are a series of tubes with fins on the outside. The fins increase the surface area for heat transfer, which increases the rate of heat exchange. Finned tubes are used in heat exchangers to transfer heat between hot and cold streams. The heat transfer rate depends on the temperature difference between the two fluids and the heat transfer coefficient between each of the fluids.
Finned tube heat exchangers are used in a variety of industries, including:
- Oil and gas
- Power generation
- Marine
- HVAC&R
Finned tube heat exchangers can be used to:
- Cool or heat fluids such as air, water, oil, or gas
- Capture or recover waste heat
- Finned tubes come in two types: transverse and longitudinal.
What is the heat transfer in tube and fins?
Heat transfer in tube and fins is a process that involves a fluid passing through tubes and conducting heat to fins. The fins then dissipate the heat to air that is blown over them. The fins increase the surface area for heat transfer, which increases the rate of heat exchange.
The amount of heat an object transfers is determined by the amount of conduction, convection, or radiation. The thermal flux is a function of both the thermal conductivity of solid parts and the convection heat coefficient between the gas and the surrounding walls. The shape and dimensions of the tubes and fins also affect the convection heat coefficient.
In an air-cooling fin-and-tube heat exchanger, heat transfers from the air flowing outside tubes to the liquid flowing inside the tubes. Because air has low thermal conductivity and density, it has poor heat transfer capability.